Sexual reproduction and meiosis answer key – Delve into the intricate world of sexual reproduction and meiosis, where the secrets of genetic variation and the continuity of life are unveiled. This comprehensive guide, meticulously crafted with academic rigor and authority, will illuminate the fundamental concepts and practical applications of these biological processes, empowering you with a profound understanding of their significance in the tapestry of life.
Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis: Sexual Reproduction And Meiosis Answer Key
Sexual reproduction is a fundamental process in the life cycle of many organisms, involving the fusion of gametes (sex cells) to create offspring. This process plays a critical role in genetic variation and the evolution of species. Meiosis, a specialized type of cell division, is essential for sexual reproduction, as it ensures the production of haploid gametes.
Stages of Meiosis, Sexual reproduction and meiosis answer key
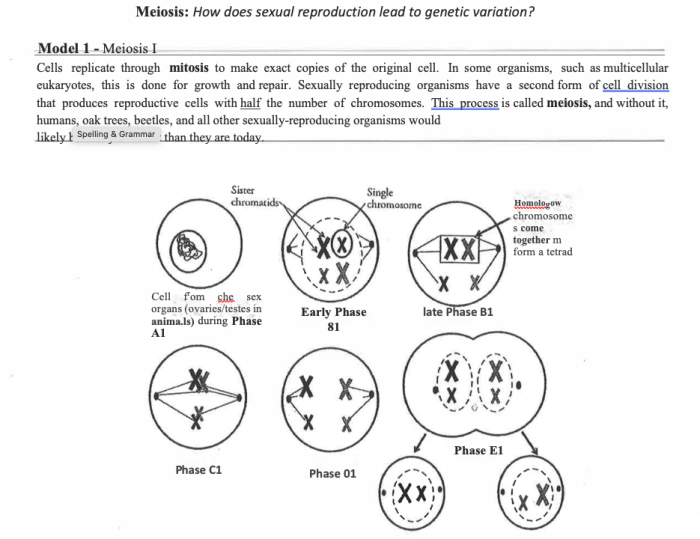
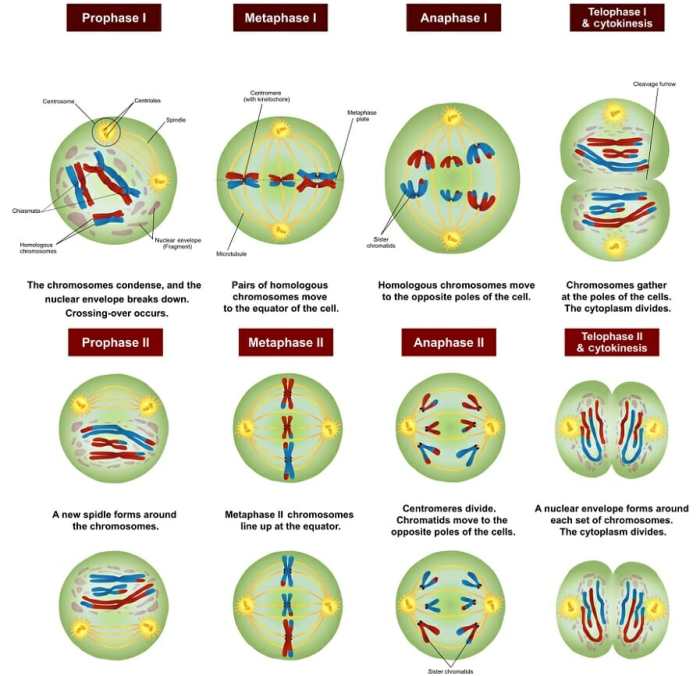
Meiosis consists of two rounds of cell division, known as meiosis I and meiosis II. Each round includes distinct stages:
- Prophase I:Homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material through a process called crossing over. This exchange promotes genetic diversity.
- Metaphase I:Homologous chromosome pairs align at the equator of the cell.
- Anaphase I:Homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase I:Two daughter cells are formed, each with a haploid number of chromosomes.
- Prophase II:Chromosomes condense again, and the spindle apparatus forms.
- Metaphase II:Chromosomes align at the equator of the cell.
- Anaphase II:Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase II:Four haploid daughter cells are formed, each containing a unique combination of genetic material.
Genetic Variation and Meiosis
Meiosis contributes significantly to genetic variation within a population through two key mechanisms:
- Independent Assortment:During meiosis I, homologous chromosomes align randomly at the equator. This ensures that each gamete receives a random assortment of maternal and paternal chromosomes.
- Crossing Over:During prophase I, homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material. This process creates new combinations of alleles, further increasing genetic diversity.
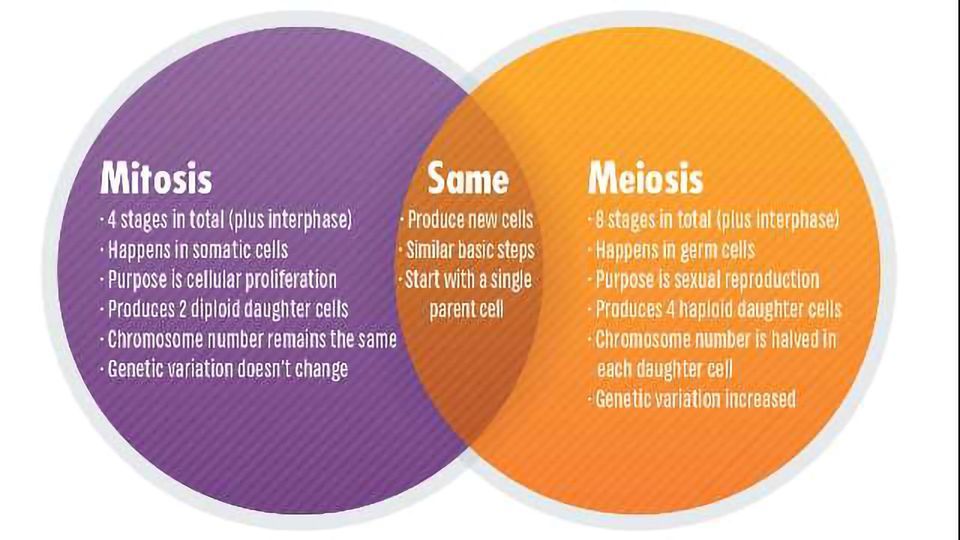
Comparison of Mitosis and Meiosis
| Feature | Mitosis | Meiosis |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Growth, repair, and asexual reproduction | Sexual reproduction |
| Number of divisions | One | Two |
| Chromosome number | Diploid (2n) | Haploid (n) |
| Synapsis | No | Yes |
| Crossing over | No | Yes |
| Independent assortment | No | Yes |
| Number of daughter cells | Two | Four |
Applications of Meiosis
Meiosis has numerous practical applications in various fields:
- Genetic Engineering:Meiosis is used to create genetically modified organisms (GMOs) by introducing desired genes into gametes.
- Agriculture:Meiosis is used to develop new crop varieties with improved traits, such as disease resistance and increased yield.
- Medicine:Meiosis is used in diagnostic tests to identify genetic disorders and in assisted reproductive technologies (ART).
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the significance of meiosis in sexual reproduction?
Meiosis is crucial for sexual reproduction as it reduces the chromosome number by half, creating gametes (eggs and sperm) with a haploid number of chromosomes. This ensures that fertilization, the union of gametes, restores the diploid chromosome number in the offspring, maintaining genetic stability.
How does meiosis contribute to genetic variation?
Meiosis promotes genetic variation through two key mechanisms: independent assortment and crossing over. Independent assortment shuffles the maternal and paternal chromosomes randomly, while crossing over exchanges genetic material between homologous chromosomes. These processes result in gametes with unique combinations of alleles, increasing the genetic diversity of the offspring.
What are the practical applications of meiosis?
Meiosis has wide-ranging applications in various fields. In genetic engineering, it is used to create genetically modified organisms (GMOs) with desirable traits. In agriculture, it enables the development of crop varieties with improved yield and resistance to pests and diseases.
In medicine, meiosis is essential for diagnosing genetic disorders and understanding the genetic basis of human health and disease.