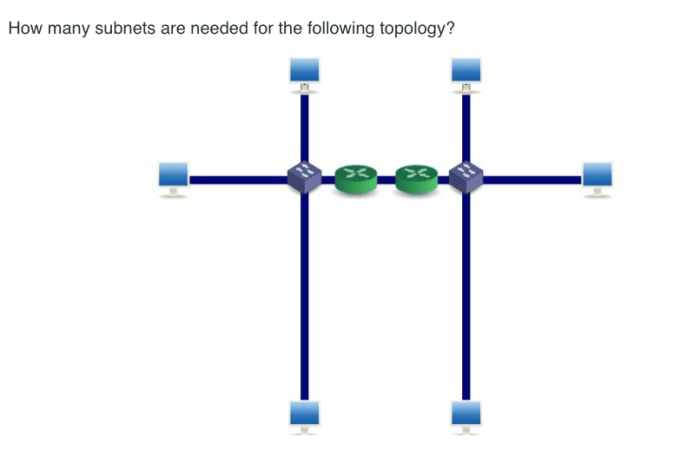
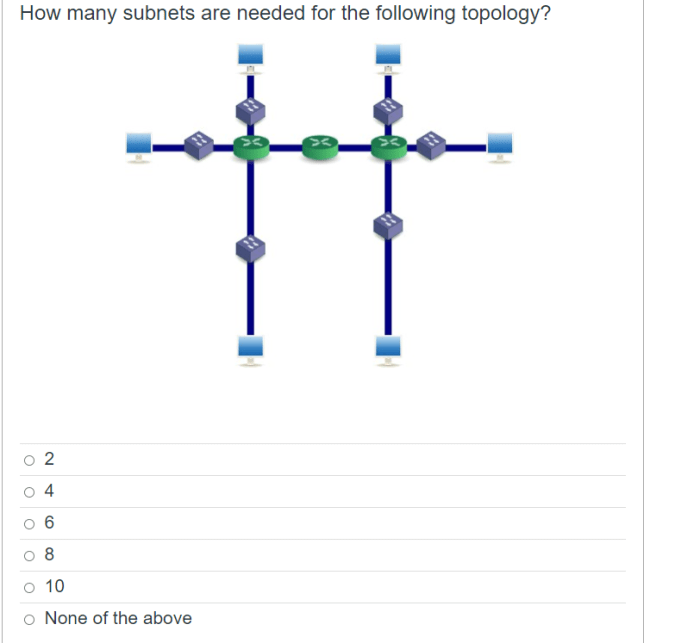
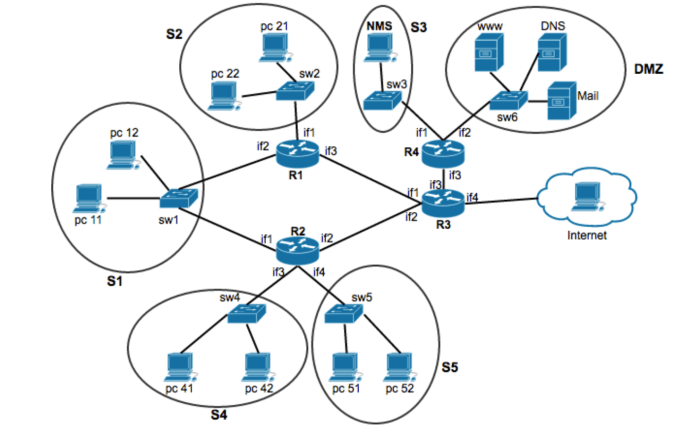
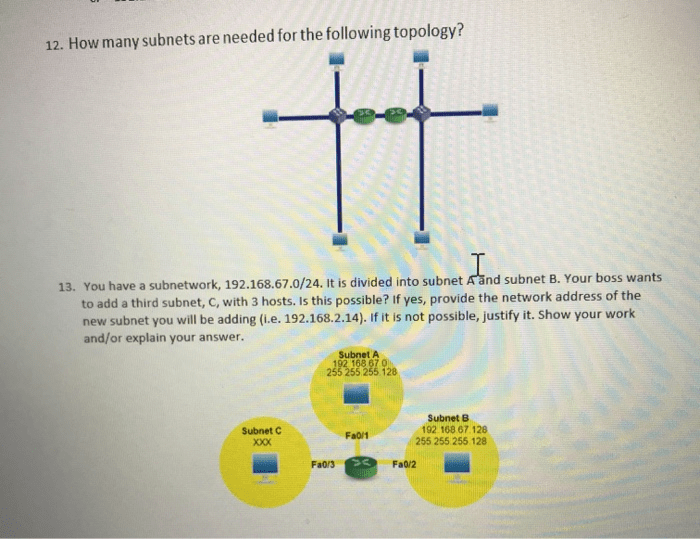
How many subnets are needed for the following topology – Subnetting, a fundamental aspect of network design, plays a crucial role in optimizing network performance and scalability. This article delves into the intricacies of subnet design, exploring the factors that determine the number of subnets required for a given network topology.
By understanding the principles and best practices of subnetting, network engineers can effectively allocate IP addresses, minimize broadcast traffic, and enhance network security.
1. Overview
Subnetting is the process of dividing a single network into smaller, more manageable subnetworks. It allows for more efficient use of IP addresses, improved network performance, and enhanced security.
The number of subnets needed depends on several factors, including the size of the network, the number of hosts, and the desired level of network security.
2. Calculating Subnet Needs
To calculate the number of subnets required, follow these steps:
- Determine the total number of hosts on the network.
- Choose a subnet mask that provides the desired number of hosts per subnet.
- Calculate the number of subnets by dividing the total number of hosts by the number of hosts per subnet.
3. Network Topology Considerations
The network topology also affects subnet design. In a bus topology, all devices are connected to a single cable. In a star topology, all devices are connected to a central hub. In a ring topology, devices are connected in a loop.
Different topologies have different subnet requirements. For example, a star topology typically requires fewer subnets than a bus topology.
4. Host Requirements
The number of hosts per subnet influences subnet design. A subnet with too many hosts can become congested, while a subnet with too few hosts can waste IP addresses.
Guidelines for determining the optimal host range for each subnet include:
- Consider the growth potential of the network.
- Avoid creating subnets with more than 254 hosts.
- Consider the security implications of having a large number of hosts on a single subnet.
5. Addressing and Routing
Subnetting plays a crucial role in IP address allocation. Subnet masks divide the IP address into two parts: the network address and the host address.
Default gateways are used to route traffic between subnets. The default gateway is the IP address of the router that connects the subnet to the rest of the network.
6. Subnet Design Best Practices, How many subnets are needed for the following topology
Best practices for subnet design include:
- Plan for growth.
- Use consistent subnet masks.
- Avoid overlapping subnets.
- Document subnet configurations.
7. Troubleshooting Subnet Issues
Common subnet design issues include:
- Incorrect subnet masks.
- Overlapping subnets.
- Incorrect default gateway configurations.
To troubleshoot subnet issues, check the following:
- Verify that the subnet masks are correct.
- Ensure that the subnets do not overlap.
- Check that the default gateway configurations are correct.
Clarifying Questions: How Many Subnets Are Needed For The Following Topology
What is the purpose of subnetting?
Subnetting divides a single network into smaller, logical subnetworks, improving network efficiency, reducing broadcast traffic, and enhancing security.
How do I determine the number of subnets needed?
The number of subnets depends on factors such as the number of hosts per subnet, the desired subnet mask, and the network topology.
What are the best practices for subnet design?
Best practices include considering growth and scalability, using hierarchical addressing, and implementing security measures such as access control lists.