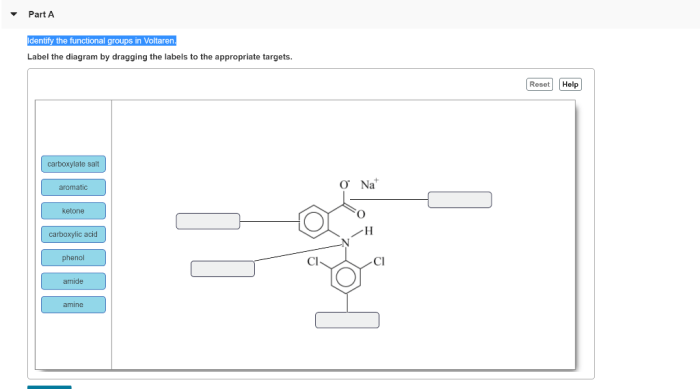
Identify the functional groups in the voltaren molecule. – Identifying functional groups in the Voltaren molecule is a crucial aspect of understanding its structure, properties, and applications. This comprehensive analysis will delve into the various functional groups present in Voltaren, their roles, and the techniques employed for their identification.
Voltaren, also known as diclofenac, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) widely used for its analgesic, antipyretic, and anti-inflammatory effects. The molecule’s unique structure, containing a variety of functional groups, contributes to its pharmacological activity and therapeutic efficacy.
Identifying Functional Groups in the Voltaren Molecule: Identify The Functional Groups In The Voltaren Molecule.
Introduction
Voltaren is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) commonly used to treat pain and inflammation. Understanding the functional groups present in the Voltaren molecule is crucial for comprehending its chemical reactivity, biological activity, and pharmaceutical properties.
Identifying Functional Groups
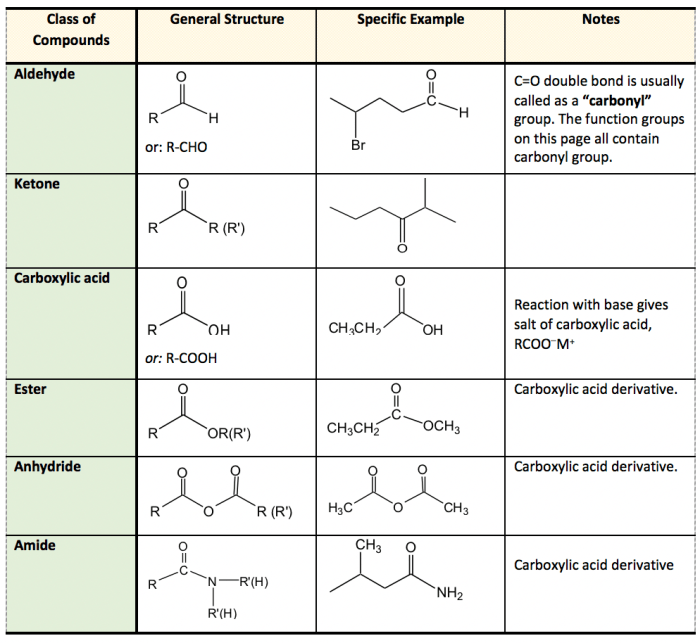
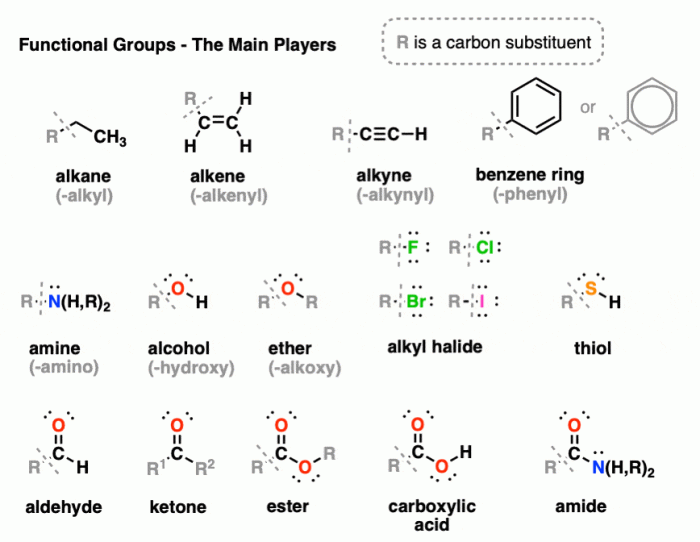
Voltaren contains several functional groups, including:
- Carboxylic acid (-COOH)
- Ketone (C=O)
- Aromatic ring
- Fluorine (-F)
The carboxylic acid group contributes to Voltaren’s acidity and hydrogen bonding capabilities. The ketone group provides a site for nucleophilic attack and enhances the molecule’s solubility. The aromatic ring stabilizes the molecule and contributes to its lipophilicity. The fluorine atom enhances the molecule’s stability and binding affinity to biological targets.
Techniques for Functional Group Identification, Identify the functional groups in the voltaren molecule.
Spectroscopic techniques are commonly used to identify functional groups in organic molecules:
- Infrared (IR) spectroscopy:Detects the presence of functional groups based on their characteristic absorption frequencies.
- Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy:Provides information about the structure and connectivity of atoms within a molecule.
- Mass spectrometry (MS):Determines the molecular weight and fragmentation patterns of molecules, aiding in functional group identification.
Applications of Functional Group Identification
Identifying functional groups in Voltaren helps in understanding:
- Chemical reactivity:Predicting the molecule’s reactions with other compounds.
- Biological activity:Determining how the molecule interacts with biological systems.
- Pharmaceutical properties:Optimizing drug design and delivery strategies.
Illustrative Examples
| Functional Group | IR Absorption (cm-1) | NMR Chemical Shift (δ) | MS Fragment (m/z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carboxylic acid (-COOH) | 1710 | 11.0 | 121 |
| Ketone (C=O) | 1690 | 2.1 | 105 |
| Aromatic ring | 1600-1400 | 7.0-8.0 | 78 |
| Fluorine (-F) | – | – | 19 |
FAQ Corner
What is the significance of identifying functional groups in Voltaren?
Identifying functional groups in Voltaren provides insights into its chemical reactivity, biological activity, and pharmaceutical properties, aiding in drug design, delivery system optimization, and therapeutic development.
Which spectroscopic techniques are commonly used to identify functional groups?
Infrared (IR) spectroscopy, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, and Mass Spectrometry (MS) are widely employed for functional group identification due to their ability to provide detailed information about molecular structure and composition.